1.5: Leveraging AI in Cyber Defense
Essential Questions
- How can AI analyze millions of network events in seconds to find a single, hidden threat?
- In what ways can AI act as a "co-pilot" for cybersecurity professionals, making their work faster and more effective?
- Why is it critical for a human to always review and approve an AI's security recommendations?
- How does AI help in the proactive discovery of vulnerabilities before an attacker can exploit them?
- What is the difference between a security rule created by a human and one suggested by an AI?
- How does the use of AI in defense create a new kind of "arms race" in cybersecurity?
Overview
Imagine you work for a company that is about to launch a new e-commerce website. The application connects to a massive warehouse inventory database, allowing customers to see real-time stock levels. Before the site goes live, your team is tasked with ensuring it's secure. The application contains hundreds of thousands of lines of code. Manually reviewing every line for potential security flaws would take weeks, if not months, and even then, a subtle mistake could be missed.
Instead of relying solely on human review, your team uses an AI-powered tool to analyze the entire codebase. The AI, trained on vast datasets of known vulnerabilities, scans the code in minutes. It flags a critical section where a user's input is being passed directly to the database—a classic opening for a SQL injection attack. The tool not only identifies the flaw but also recommends a specific, secure way to rewrite the code. The development team reviews the AI's suggestion, confirms its validity, and implements the fix. The company avoids a potentially devastating data breach before a single customer is onboarded.
This scenario illustrates the transformative power of artificial intelligence in cyber defense. While the previous lesson explored how adversaries use AI, this lesson focuses on the other side of the coin: how "blue teams" (defenders) are leveraging AI as a force multiplier. You'll learn how AI is used to proactively harden systems, sift through mountains of data to detect threats in real-time, and help human analysts respond to incidents with greater speed and precision. This is the future of cybersecurity, where human expertise is augmented by the analytical power of machines.
Using AI to Proactively Protect Systems (1.5.A)
One of the most significant advantages of AI in cybersecurity is its ability to shift defenders from a reactive to a proactive posture. Instead of waiting for an attack to happen, security teams can use AI to identify and fix weaknesses before they can be exploited. This proactive hardening of networks, applications, and data is a cornerstone of modern defense-in-depth strategies.
As seen in the overview, AI-powered code analysis is a prime example. Tools trained on countless examples of both secure and insecure code can scan an application's source code to find vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), or insecure direct object references. They can then provide developers with concrete recommendations for mitigation. This doesn't replace the need for knowledgeable programmers; rather, it acts as a tireless assistant that catches potential issues humans might miss. The key to success is the partnership: the AI flags a problem and suggests a solution, but a human expert must always review the recommendation to ensure it's appropriate for the context and doesn't introduce other problems.
AI can also be used to optimize and validate security configurations. A large organization's network might have thousands of firewall rules and complex access control lists. It's easy for these configurations to become outdated or contain errors that create security holes. An AI tool can analyze these rule sets, compare them against security best practices and known threats, and recommend changes. For example, it might identify a firewall rule that is too permissive or an access control policy that grants a user unnecessary privileges. By flagging these issues, the AI helps security technicians maintain a more secure and hardened network posture.
Furthermore, AI can help generate better rules for detection systems. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems rely on rules to identify malicious activity. Crafting effective rules requires deep expertise. AI can analyze historical data and threat intelligence feeds to suggest new, more nuanced detection rules that are better at spotting the subtle signs of an emerging attack. Again, these AI-generated rules must be reviewed and approved by a human detection engineer before being deployed, ensuring that they are accurate and don't create a flood of false positives.
An interactive "AI Code Review" simulation named "1.5-code-scanner". The UI shows a snippet of vulnerable code (e.g., a simple PHP script with a SQL injection flaw). The learner clicks a "Scan with AI" button. The AI highlights the vulnerable line and displays a pop-up with two elements: (1) an explanation of the vulnerability, and (2) a recommended, secure code snippet that uses parameterized queries. This demonstrates the proactive, advisory role of AI in development.
<?php
// User login form handler
$username = $_POST['username'];
$password = $_POST['password'];
// Check user credentials
$query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '$username' AND password = '$password'";
$result = mysqli_query($connection, $query);
if (mysqli_num_rows($result) > 0) {
echo "Login successful!";
$_SESSION['user'] = $username;
} else {
echo "Invalid credentials!";
}
?><?php
// User login form handler - SECURE VERSION
$username = $_POST['username'];
$password = $_POST['password'];
// Validate input
if (empty($username) || empty($password)) {
echo "Username and password are required!";
exit;
}
// Use prepared statements to prevent SQL injection
$stmt = $connection->prepare("SELECT id, username, password_hash FROM users WHERE username = ?");
$stmt->bind_param("s", $username);
$stmt->execute();
$result = $stmt->get_result();
if ($result->num_rows === 1) {
$user = $result->fetch_assoc();
// Verify password using secure hashing
if (password_verify($password, $user['password_hash'])) {
echo "Login successful!";
session_start();
$_SESSION['user_id'] = $user['id'];
$_SESSION['username'] = $user['username'];
} else {
echo "Invalid credentials!";
}
} else {
echo "Invalid credentials!";
}
$stmt->close();
?>🤖 AI Advantages:
- Analyzes thousands of lines of code in seconds
- Detects subtle vulnerabilities humans might miss
- Provides instant feedback during development
- Suggests specific fixes and secure alternatives
- Learns from known vulnerability databases
👥 Human Oversight Still Required:
- AI may produce false positives requiring review
- Context-specific security decisions need human judgment
- AI suggestions must be validated before implementation
- Business logic vulnerabilities may require human insight
- Security policies and compliance need human oversight
Proactive Security: AI code scanners integrate with development environments to catch vulnerabilities before code reaches production, significantly reducing security risks.
Developer Education: By explaining vulnerabilities and suggesting fixes, AI tools help developers learn secure coding practices and avoid similar mistakes in the future.
Continuous Monitoring: AI can continuously scan code repositories, alerting security teams to new vulnerabilities as they're introduced or discovered.
Enabling Faster and More Accurate Threat Detection (1.5.B)
A modern corporate network generates a staggering amount of data. Every login, file access, email sent, and website visited creates a digital event. For a large organization, this can mean millions or even billions of events per day. Buried within this ocean of data are the faint signals of malicious activity. It is humanly impossible to manually examine every event. This is where AI's ability to analyze data at scale becomes a game-changer for threat detection and response.
AI-powered tools, particularly those using machine learning, can be trained to understand what "normal" activity looks like on a network. They build a baseline model of typical user behavior, network traffic patterns, and system processes. Once this baseline is established, the AI can monitor the network in real-time and flag anomalies that deviate from the norm. For example, it might detect a user account that normally logs in from one country suddenly attempting to access the system from another, or a server that suddenly starts communicating with a known malicious IP address. These anomalies are surfaced to human analysts for investigation.
This process allows security teams to sort likely malicious events from harmless ones with incredible speed and accuracy. Instead of drowning in raw data, human analysts are presented with a prioritized list of the most suspicious activities. This allows them to focus their expertise where it's needed most, investigating high-probability threats instead of chasing down countless false alarms. The AI acts as a sophisticated filter, turning an unmanageable firehose of data into a focused stream of actionable intelligence.
This leads to a much faster response. When a likely threat is detected, AI-powered systems can even initiate automated responses. Based on pre-defined playbooks, the system might automatically isolate a compromised device from the network to prevent malware from spreading, or temporarily block an IP address that is sending malicious traffic. These automated actions are designed to contain a threat in its earliest stages, buying valuable time for human responders to conduct a deeper investigation and eradicate the threat. This combination of AI-powered detection and automated response enables organizations to catch and intervene in attacks much more quickly, minimizing potential damage and disruption.
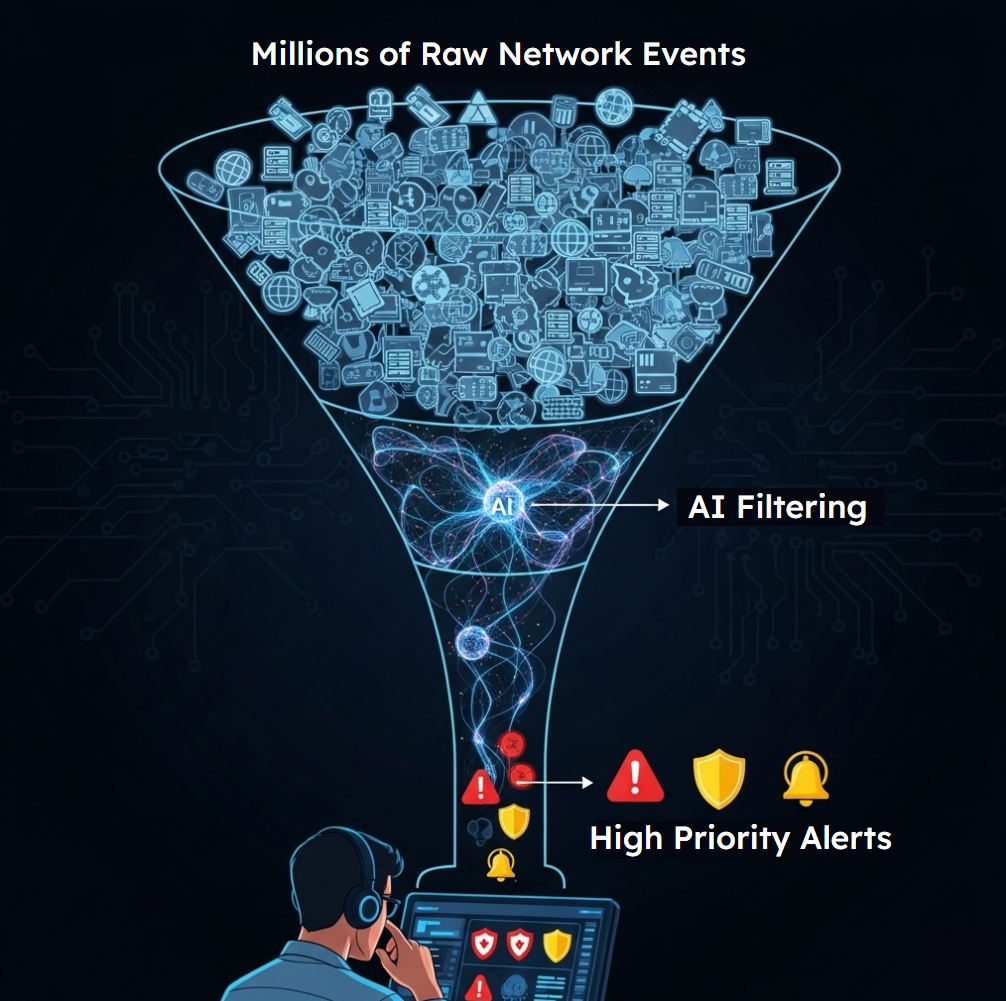
A "Threat Hunting Dashboard" simulation named "1.5-threat-dashboard". The UI displays a live-updating feed of network events (e.g., logins, file transfers). The feed is scrolling too fast to read. The learner can toggle an "AI Anomaly Detection" switch. When on, the feed is filtered, and only a few suspicious events are highlighted (e.g., "Login from unusual location," "Large data exfiltration detected"). Clicking an alert provides a short summary of why the AI flagged it, demonstrating how AI helps analysts focus on what matters.
Click "Start Monitoring" to begin network event simulation
With AI Anomaly Detection:
- • Filters out 99%+ of normal traffic automatically
- • Surfaces only high-priority security events
- • Provides context and reasoning for each alert
- • Enables human analysts to focus on real threats
- • Dramatically reduces investigation time
- • Scales to handle millions of events per day
Without AI (Traditional Approach):
- • Analysts overwhelmed by event volume
- • Critical threats buried in normal traffic
- • High false positive rates
- • Delayed response to actual attacks
- • Requires large security teams
- • Human error due to information overload
Real-World Impact:
Modern AI-powered security operations centers (SOCs) can process billions of events daily, automatically prioritizing the most critical threats. This allows security teams to respond to attacks in minutes rather than hours or days, significantly reducing potential damage.
Further Reading & Resources
- IBM: What is AI in cybersecurity?
- Microsoft Security: The Role of AI in Cybersecurity
- CSO Online: How AI is being used for cybersecurity
- Gartner: AI for Cybersecurity